C++ 선형 자료 구조
Contiguous vs Non-contiguous data structures
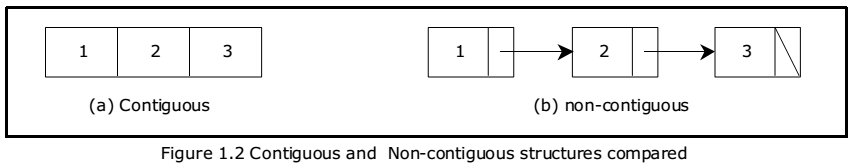
- 이미지 출처
Continguous data structure
std::array,std::vector…- 모든 데이터 원소가 연속된 형태로 저장됨.
- 첫번째 데이터 원소의 메모리 주소를 Base address라고 함.
- 데이터 원소에 곧바로 접근 가능 (
). BA + i * sizeof(type)
- Cache locality: 데이터 원소에 접근할 때 주변 원소들도 함께 cache로 가져옴.
- 메모리에서 접근하는 것 보다 cache에서 접근하는 것이 몇십~몇백배 더 빠름.
- Static 형태와 Dynamic 형태로 할당 가능.
- Static: Stack에 할당
int arr[size]
- Dynamic: Heap에 할당
int* arr = new int[size]
- Static: Stack에 할당
Non-contiguous data structure
std::list,std::forward_list…- 여러 다른 위치에 데이터가 저장됨.
- Linked list (위 이미지의 오른쪽에 그려진 자료구조)
- 여러 node로 구성됨.
- 각각의 node는 데이터 + 다음 node를 가리키는 pointer로 구성됨.
- 데이터 원소에 접근하려면
이 필요함. - head -> node -> node -> node…를 통해 i번 이동해야함.
- 데이터 원소의 삽입/삭제가 빠름 (
) - Cache locality를 기대할 수 없음.
- 데이터 원소가 연속되어있지 않기 때문.
Comparison
| Contiguous | Non-contiguous | |
|---|---|---|
| Random element access | ||
| push_back() | ||
| insert() | ||
| cache locality | Y | N |